Introducción a la fibra de carbono en aplicaciones automotrices
¿Qué hace que la fibra de carbono sea esencial en el diseño de vehículos modernos?
-
La fibra de carbono es un material liviano pero increíblemente resistente que ha revolucionado el diseño automotriz, particularmente en aplicaciones de alto rendimiento y deportes de motor.
-
Desarrollada inicialmente para uso aeroespacial y militar, la fibra de carbono se ha convertido en un material predilecto para la reducción de peso, la resistencia y la estética en vehículos de alto rendimiento y de lujo.
-
Se utiliza comúnmente para paneles de carrocería, componentes aerodinámicos, molduras interiores y refuerzos estructurales.
Por qué es importante la selección de materiales: Cómo equilibrar rendimiento, estética y coste
-
Beneficios de rendimiento: La relación resistencia-peso de la fibra de carbono supera a los materiales tradicionales como el acero y el aluminio, reduciendo el peso del vehículo y mejorando la velocidad, la eficiencia del combustible y el manejo.
-
Atractivo estético: Los patrones tejidos y acabados únicos de la fibra de carbono brindan a los vehículos un aspecto agresivo y de alta gama, lo que la convierte en una opción popular tanto para la personalización de equipos originales como para el mercado de accesorios.
-
Consideraciones de costo: Si bien la fibra de carbono ofrece beneficios incomparables, los diferentes tipos varían en precio, complejidad de fabricación y durabilidad. Elegir el tipo correcto puede influir en la inversión total en una construcción.
¿Qué factores definen la resistencia, durabilidad y valor de la fibra de carbono?
Patrón de tejido
-
La integridad estructural y el atractivo visual de la fibra de carbono dependen en gran medida del patrón del tejido, lo que influye tanto en la flexibilidad como en la rigidez.
-
Los diferentes tejidos ofrecen distintos niveles de resistencia, apariencia y ventajas específicas para cada aplicación.
Resistencia y durabilidad
-
La fibra de carbono es conocida por su alta resistencia a la tracción, pero los diferentes métodos de producción y aplicaciones de resina afectan su resistencia al impacto, la flexión y el desgaste a largo plazo.
-
Comprender cómo se comparan los diferentes tipos en cuanto a resistencia es fundamental para seleccionar el material adecuado para aplicaciones de alto estrés.
Peso y eficiencia
-
Una de las mayores ventajas de la fibra de carbono es su capacidad de proporcionar una resistencia excepcional con una fracción del peso de los metales tradicionales.
-
Los diferentes tipos de compuestos de fibra de carbono varían en cuanto a ahorro de peso, lo que hace que la selección del material sea importante para construcciones orientadas al rendimiento.
Proceso de fabricación
-
La forma en que se fabrica la fibra de carbono (ya sea mediante procesos de tejido tradicionales, técnicas de forjado o combinaciones híbridas) afecta su costo, resistencia y facilidad de aplicación.
-
Las diferencias de fabricación también determinan si el material es adecuado para refuerzo estructural, paneles de carrocería o modificaciones puramente estéticas.
Costo y accesibilidad
-
La fibra de carbono de alta gama, como el carbono seco preimpregnado, ofrece una resistencia superior y un peso menor, pero tiene un precio superior.
-
Alternativas más asequibles, como la fibra de carbono húmeda, ofrecen una estética similar pero con menor durabilidad y mayor peso.
-
Sopesar los costos frente a los beneficios es esencial para determinar la mejor opción para cualquier construcción o aplicación.
La ciencia detrás de la fibra de carbono: comprensión de su resistencia y proceso de fabricación
¿Cómo se fabrica la fibra de carbono? De la materia prima al compuesto de alto rendimiento
La producción de fibra de carbono es un proceso complejo que transforma las materias primas en un compuesto liviano y de alta resistencia que se utiliza en aplicaciones automotrices, aeroespaciales e industriales.
Materias primas y formación de fibras
-
La fibra de carbono comienza como un material a base de polímero, normalmente poliacrilonitrilo (PAN), aunque también se pueden utilizar rayón y brea de petróleo.
-
Las fibras de PAN se someten a un tratamiento de alta temperatura en un ambiente libre de oxígeno, un proceso llamado carbonización, que elimina los elementos no carbonados y fortalece las fibras.
-
El resultado son filamentos extremadamente finos, de entre 5 y 10 micrones de diámetro, que se agrupan para formar haces (grupos de filamentos utilizados para tejer o moldear).
¿Cómo afectan los patrones de tejido la resistencia y la flexibilidad?
-
Los filamentos de fibra de carbono se tejen en láminas de tela o se combinan en estructuras no tejidas, dependiendo de la aplicación.
-
Diferentes técnicas de tejido inciden en la rigidez, flexibilidad y atractivo estético de la fibra, razón por la cual existen diversos patrones en aplicaciones automotrices.
Impregnación de resina y formación de compuestos
-
Para crear un compuesto utilizable, las láminas de fibra de carbono deben combinarse con resina, que une las fibras y determina la resistencia, el peso y la durabilidad del producto final.
-
Esta combinación de fibra de carbono y resina es lo que forma el plástico reforzado con fibra de carbono (CFRP), el material utilizado en los componentes de los vehículos.
Comparación completa de los tipos de fibra de carbono
¿Es la fibra de carbono con tejido de sarga 2x2 la mejor en cuanto a resistencia, estilo y versatilidad? 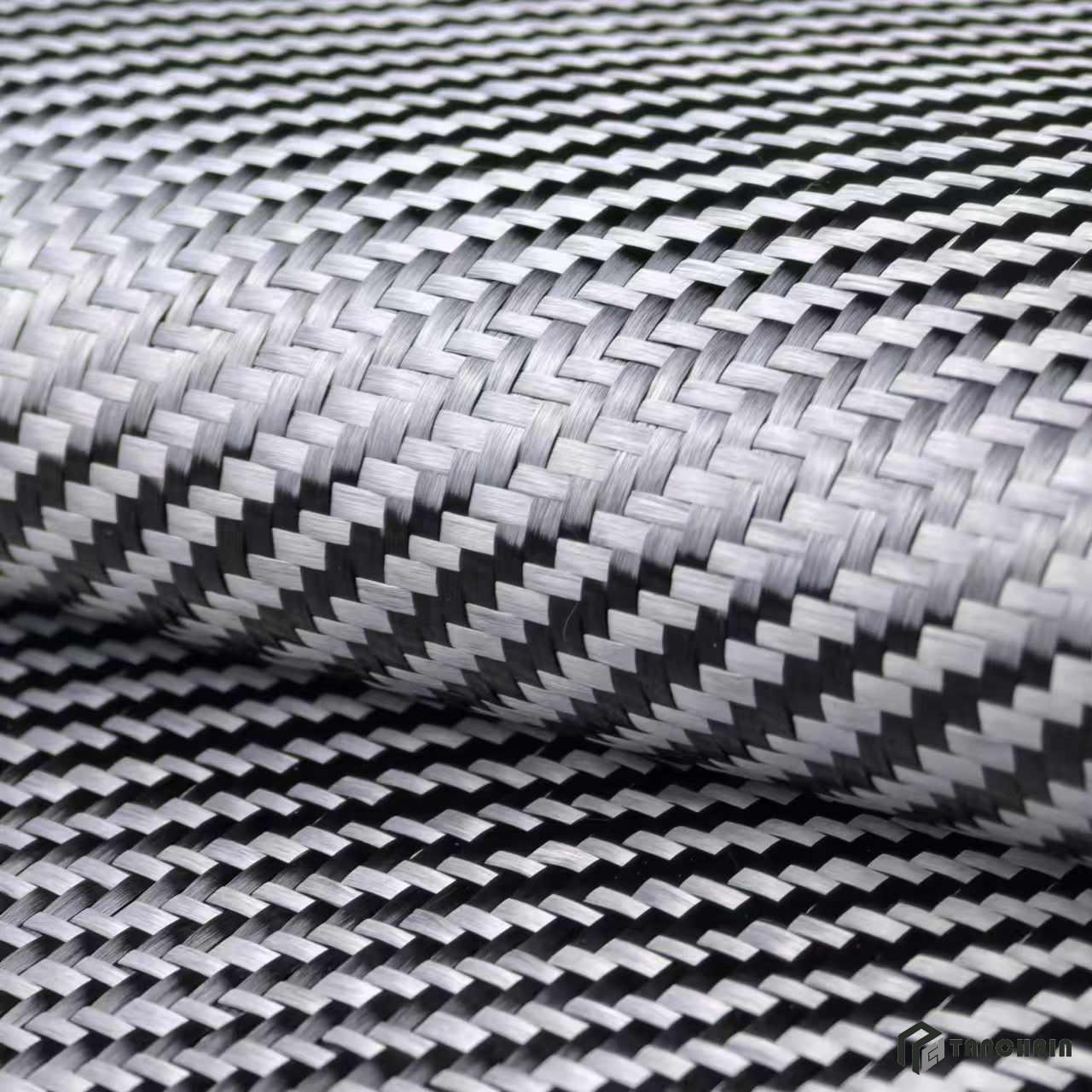
Composición estructural y patrón de tejido
-
Presenta un patrón de tejido diagonal, donde dos fibras corren por encima y dos por debajo, creando una apariencia estructurada y uniforme.
-
El tejido de sarga mejora la flexibilidad manteniendo una alta resistencia a la tracción, lo que lo hace ideal para aplicaciones que requieren un equilibrio entre rigidez y adaptabilidad.
-
Disponible en acabados brillantes o mate, donde el brillo ofrece un aspecto profundo y brillante, mientras que el mate proporciona una estética más discreta y moderna.
Proceso de fabricación y cómo afecta a la rigidez
-
Fabricado con preimpregnado (carbono seco) o carbono húmedo tradicional, según el costo y los requisitos de la aplicación.
-
El tejido de sarga permite cierta flexibilidad al tiempo que mantiene una alta resistencia direccional, lo que lo hace más resistente que el carbono forjado en aplicaciones de soporte de carga.
-
El contenido de resina y el método de curado (autoclave vs. bolsa de vacío) influyen significativamente en la rigidez final, el peso y la durabilidad.
Relación resistencia-peso en comparación con otros tipos de fibra de carbono
-
Mayor resistencia a la tracción que el carbono forjado, ya que las hebras de fibra continuas refuerzan el material en múltiples direcciones.
-
Mayor rigidez e integridad estructural, lo que lo convierte en la opción preferida para componentes de chasis, elementos aerodinámicos y refuerzos estructurales.
-
El peso es bajo en comparación con la fibra de vidrio o el aluminio, y comparable o más liviano que el carbono forjado, dependiendo de la aplicación de resina.
Aplicaciones automotrices comunes
-
Se utiliza en paneles de carrocería, capós, baúles, divisores, faldones laterales y componentes interiores.
-
Se ve con frecuencia en aplicaciones de rendimiento de OEM y de posventa, incluido el refuerzo del chasis, las actualizaciones aerodinámicas y los componentes del compartimiento del motor.
-
Preferido en deportes de motor y autos de calle de alto rendimiento donde la resistencia y el ahorro de peso son fundamentales.
Pros y contras en términos de costo, durabilidad y estética
Ventajas:
-
Mayor resistencia a la tracción y rigidez que el carbono forjado, lo que lo hace mejor para aplicaciones estructurales.
-
Aspecto clásico de fibra de carbono de alto rendimiento, reconocido en toda la industria.
-
Buen equilibrio entre resistencia y flexibilidad, lo que permite una variedad de usos.
-
Disponible en acabados brillantes y mate, satisfaciendo diferentes preferencias de diseño.
-
Costo moderado en comparación con el carbono forjado, lo que lo hace accesible para muchos entusiastas y constructores.
Contras:
-
Menos resistente al impacto que el carbono forjado, lo que significa que puede agrietarse bajo tensión extrema o fuerzas de colisión.
-
Más rígido pero menos adaptable a formas complejas, requiriendo un moldeado preciso para su ajuste.
-
Común en la industria, por lo que carece de la singularidad de las variaciones más exóticas de fibra de carbono.
¿Qué es la fibra de carbono forjada? Intercambios entre estética y rendimiento 
Proceso de fabricación y diferencias clave con la fibra de carbono tejida
-
Se fabrica comprimiendo hebras de fibra de carbono cortadas con resina en un molde de alta presión, en lugar de tejer fibras continuas.
-
Utiliza tecnología preimpregnada, lo que garantiza una distribución uniforme de la resina y una fuerte unión interna.
-
La orientación aleatoria de las fibras elimina los puntos débiles en direcciones específicas, lo que crea una alta resistencia al impacto pero una menor rigidez general en comparación con la fibra de carbono tejida.
Propiedades de resistencia y resistencia al impacto
-
Más resistente al impacto que la fibra de carbono tejida, dispersando la fuerza en múltiples orientaciones de la fibra.
-
Menor resistencia a la tracción y rigidez en comparación con el tejido de sarga, lo que lo hace inadecuado para componentes estructurales portantes.
-
Ideal para piezas cosméticas y no estructurales donde la dureza y la durabilidad importan más que la rigidez.
Atractivo estético y potencial de personalización
-
El patrón de fibra aleatoria y jaspeada crea una estética moderna y de alta tecnología distinta de la fibra de carbono tejida tradicional.
-
Debido a su fabricación única, cada pieza tiene un patrón ligeramente diferente, lo que aumenta su exclusividad.
-
Disponible en acabados mate y brillante, siendo el mate el más común para una apariencia cruda y centrada en el rendimiento.
Comparación de peso con otros tipos de fibra de carbono
-
Más ligero que la fibra de carbono húmeda estándar, pero no necesariamente más ligero que el carbono sarga preimpregnado 2x2.
-
El ahorro de peso depende del contenido de resina y de la eficiencia de compresión durante la fabricación.
Aplicaciones en deportes de motor, coches de lujo y piezas de recambio
-
Se utiliza en superdeportivos, hiperdeportivos y vehículos de alto rendimiento, incluidas aplicaciones de Lamborghini, McLaren y Pagani.
-
Común en volantes, tapas de espejos, piezas aerodinámicas y paneles de revestimiento interior debido a su estética distintiva.
-
Se encuentra en áreas propensas a impactos donde se prioriza la dureza sobre la rigidez, como umbrales de puertas y paneles interiores.
Pros y contras en cuanto a costo, rigidez y facilidad de uso
Ventajas:
-
Resistencia al impacto superior en comparación con la fibra de carbono tejida, lo que reduce el riesgo de agrietamiento.
-
Aspecto visualmente único, que lo hace destacar en construcciones personalizadas de alta gama.
-
Menor desperdicio de fabricación, lo que a veces puede reducir los costos de producción a gran escala.
Contras:
-
Menor resistencia a la tracción y rigidez que el carbono sarga, lo que lo hace inadecuado para aplicaciones estructurales.
-
Más caro que la fibra de carbono tejida tradicional, especialmente para aplicaciones personalizadas.
-
Tiene más contenido de resina que el carbono tejido, lo que a veces puede aumentar el peso si no se fabrica de manera eficiente.
¿Cuándo usar un híbrido de carbono y kevlar? Mejores aplicaciones para protección contra impactos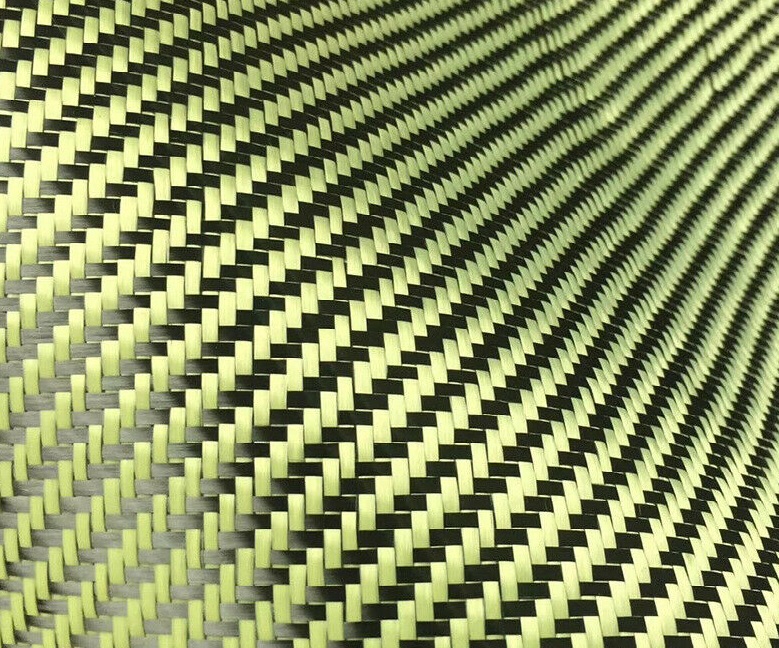 
Composición: Mezcla de fibra de carbono con fibras de Kevlar
-
Un material híbrido que combina la resistencia de la fibra de carbono con la resistencia al impacto del Kevlar.
-
Generalmente presenta capas alternas de fibra de carbono y Kevlar o hebras tejidas de Kevlar integradas en la tela de fibra de carbono.
Ventajas de resistencia al impacto y a la fuerza
-
Más resistente al agrietamiento o rotura por impacto en comparación con la fibra de carbono pura.
-
Mayor flexibilidad, lo que lo hace ideal para aplicaciones que requieren cierta flexibilidad en lugar de rigidez extrema.
-
Mantiene propiedades livianas al tiempo que agrega una resistencia a la abrasión mejorada.
Consideraciones de peso en comparación con la fibra de carbono pura
-
Un poco más pesado que la fibra de carbono tradicional, pero el aumento de peso es mínimo en comparación con los beneficios adicionales en durabilidad.
-
Proporciona un punto medio entre la rigidez de la fibra de carbono y la dureza del Kevlar.
Variaciones de color y atractivo estético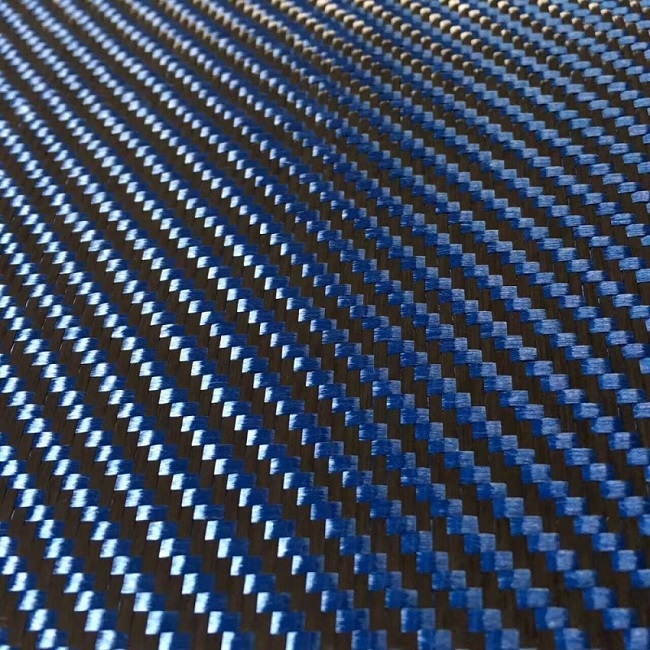 
-
A menudo disponible en combinaciones de colores distintivas, como negro y dorado, negro y rojo o negro y azul, debido al color natural del Kevlar.
-
Se utiliza en aplicaciones personalizadas y de carreras tanto por su atractivo estético como por su funcionalidad.
Usos comunes en aplicaciones automotrices y de deportes de motor
-
Se encuentra en áreas de alto impacto, como protección de bajos, huecos de ruedas y paneles reforzados.
-
Se utiliza frecuentemente en motocicletas y aplicaciones de carreras todoterreno donde la durabilidad es crucial.
-
A veces se utiliza en asientos, paneles de puertas y otras aplicaciones interiores para lograr una apariencia agresiva y de alto rendimiento.
Pros y contras en cuanto a costo, flexibilidad y resistencia al desgaste
Ventajas:
-
Mayor resistencia al impacto que la fibra de carbono pura.
-
Atractivo estético distintivo con opciones de color.
-
Mayor flexibilidad que los tejidos rígidos de fibra de carbono.
Contras:
-
Un poco más pesado que la fibra de carbono estándar.
-
Más caro que la fibra de carbono tejida tradicional debido a la combinación de materiales.
-
Disponibilidad limitada en las principales aplicaciones del mercado de accesorios.
¿Existen otros tejidos de fibra de carbono? Explorando el tejido liso, el panal y más
Tejido liso de fibra de carbono (1x1)
-
Patrón de tejido más simple, con fibras tejidas en una estructura básica de arriba a abajo.
-
Más rígido que el tejido de sarga pero menos flexible, lo que lo hace ideal para superficies planas o simples.
-
Menor costo, pero menos dinámico visualmente en comparación con la sarga o el carbono forjado.
4x4 y otros tejidos de sarga 
-
Similar a la sarga 2x2 pero con espacios más grandes entre las hebras del tejido, lo que proporciona mayor flexibilidad.
-
Se utiliza en aplicaciones donde las superficies curvas requieren mayor adaptabilidad.
Fibra de carbono en forma de panal 
-
Cuenta con una estructura de núcleo liviana intercalada entre capas de fibra de carbono, lo que proporciona una resistencia excepcional sin exceso de peso.
-
Se utiliza en aplicaciones estructurales, aeroespaciales y componentes de deportes de motor de alta gama.
Factores clave a considerar al elegir fibra de carbono
¿Qué tipo de fibra de carbono ofrece la mejor resistencia y durabilidad para la integridad estructural?
-
Fibra de carbono de tejido sarga 2x2: ofrece alta resistencia a la tracción y rigidez, lo que la convierte en la mejor opción para aplicaciones estructurales como paneles de carrocería, refuerzos de chasis y componentes aerodinámicos.
-
Fibra de carbono forjada: proporciona una alta resistencia al impacto debido a sus fibras orientadas aleatoriamente, pero carece de la resistencia direccional y la rigidez de la fibra de carbono tejida, lo que la hace más adecuada para aplicaciones cosméticas y sin carga.
-
Híbrido de carbono y kevlar: Excelente para zonas propensas a impactos, ya que el kevlar mejora la resistencia a la abrasión y la dureza, manteniendo un peso relativamente bajo. Ideal para la protección de bajos, pasos de rueda y zonas reforzadas.
Factores que afectan la durabilidad
-
Contenido de resina: Los procesos de fabricación de mayor calidad garantizan una distribución uniforme de la resina, lo que mejora la durabilidad a largo plazo y evita la delaminación.
-
Método de curado: La fibra de carbono curada en autoclave es significativamente más resistente que las alternativas envasadas al vacío o colocadas en húmedo.
-
Exposición a los elementos: la fibra de carbono es resistente a la corrosión, pero puede degradarse bajo la exposición a los rayos UV si no se recubre adecuadamente, lo que hace que una capa transparente resistente a los rayos UV sea esencial para una durabilidad a largo plazo.
¿Cuánto peso puede ahorrar la fibra de carbono? Encontrando la mejor opción para rendimiento y eficiencia.
-
Fibra de carbono de tejido sarga 2x2: ligero y resistente, lo que lo convierte en un gran equilibrio entre reducción de peso y rigidez.
-
Fibra de carbono forjada: más liviana que el carbono húmedo estándar, pero a menudo con mucha resina, lo que puede aumentar el peso dependiendo de la calidad de fabricación.
-
Híbrido de carbono y kevlar: un poco más pesado que la fibra de carbono pura, pero proporciona protección adicional contra impactos, lo que lo convierte en un equilibrio entre peso y durabilidad.
Por qué es importante bajar de peso
-
Un peso menor mejora la aceleración, el manejo y el rendimiento de frenado.
-
La distribución del peso es fundamental en las construcciones de alto rendimiento, y los materiales más livianos mejoran el equilibrio y la eficiencia generales.
-
Los componentes estructurales se benefician más de los materiales más livianos, lo que reduce la tensión innecesaria en las piezas de soporte.
¿Qué estilo de fibra de carbono combina con tu diseño? Consideraciones estéticas para autos de calle y de carreras
-
Fibra de carbono de tejido de sarga 2x2: el patrón clásico y reconocible de fibra de carbono con un aspecto elegante y de alto rendimiento.
-
Fibra de carbono forjada: proporciona una apariencia única y jaspeada, a menudo utilizada en superdeportivos y construcciones personalizadas para una estética moderna y de alta tecnología.
-
Híbrido de carbono y kevlar: presenta patrones tejidos con variaciones de color, como negro y dorado, negro y rojo o negro y azul, lo que le da una apariencia distintiva y agresiva.
-
Acabados brillantes vs. mate:
-
El acabado brillante realza la profundidad y el brillo, y se observa comúnmente en piezas exteriores de la carrocería y componentes decorativos.
-
El acabado mate proporciona una apariencia discreta y sigilosa, a menudo preferida para acabados interiores y construcciones de alto rendimiento.
Mejores aplicaciones para el impacto estético
-
El tejido de sarga clásico es ideal para un estilo atemporal y de alta gama.
-
El carbono forjado es ideal para una estética personalizada y de alta tecnología.
-
El Kevlar de carbono agrega un contraste de color único, lo que lo hace popular en los deportes de motor y en las construcciones agresivas.
¿Por qué es tan cara la fibra de carbono? Costo y disponibilidad explicados
-
Fibra de carbono de tejido sarga 2x2: la opción más disponible y rentable debido a su producción en masa y versatilidad.
-
Fibra de carbono forjada: más cara que el tejido de sarga debido a su complejo proceso de fabricación, pero la disponibilidad está aumentando a medida que más empresas la adoptan.
-
Híbrido de carbono y kevlar: menos común y normalmente más caro, ya que implica mezclar dos materiales, lo que aumenta los costos de producción.
Factores que afectan el precio de la fibra de carbono
-
Complejidad de producción: Cuanto más intrincado sea el proceso de tejido y curado, mayor será el costo.
-
Disponibilidad de materia prima: Las fibras de carbono con infusión de Kevlar tienen costos de material más altos que la fibra de carbono tejida estándar.
-
Demanda del mercado: El tejido de sarga se produce ampliamente, lo que lo convierte en la opción más asequible, mientras que los híbridos de carbono forjado y Kevlar son más especializados, lo que aumenta su precio.
¿Cuál es la mejor fibra de carbono para instalación profesional o casera?
-
Fibra de carbono de tejido de sarga 2x2: la más fácil de trabajar debido a la dirección constante de la fibra y su flexibilidad, lo que la hace adecuada para instalaciones de bricolaje y piezas prefabricadas.
-
Fibra de carbono forjada: más difícil de moldear y modificar después de la producción, lo que requiere una fabricación precisa y una instalación profesional.
-
Híbrido de carbono y kevlar: más difícil de cortar y dar forma, ya que las fibras de kevlar son resistentes a la abrasión, lo que dificulta el recorte y la perforación sin herramientas especializadas.
Las mejores opciones para proyectos de bricolaje
-
Paneles de fibra de carbono con tejido sarga y piezas precortadas.
-
Carbono forjado para componentes atornillados directamente, como molduras y tapas de espejos.
Cuándo optar por una instalación profesional
-
Si modifica o corta Kevlar de carbono (debido a la resistencia de la fibra de Kevlar).
-
Si lograr un acabado uniforme y de alta calidad es una prioridad.
Rendimiento vs. uso en calle: ¿Cómo elegir la fibra de carbono adecuada?
-
Fibra de carbono de tejido sarga 2x2: ideal para construcciones de alto rendimiento, refuerzos de chasis y componentes aerodinámicos.
-
Fibra de carbono forjada: más adecuada para exhibiciones, autos de lujo y aplicaciones cosméticas que para uso estructural.
-
Híbrido de carbono y kevlar: ideal para autos de carrera, vehículos todoterreno y aplicaciones de alto impacto donde la durabilidad es fundamental.
Consideraciones clave sobre rendimiento y estética
-
Las construcciones callejeras se centran más en la estética, el coste y la facilidad de instalación.
-
Los autos de carreras requieren relaciones resistencia-peso superiores y resistencia al impacto.
-
Las construcciones de lujo priorizan materiales únicos como el carbono forjado para lograr exclusividad.
Las mejores opciones de fibra de carbono por aplicación
|
Solicitud |
El mejor tipo de fibra de carbono |
|
Refuerzos del chasis |
Sarga 2x2 |
|
Componentes aerodinámicos |
Sarga 2x2 |
|
Acabado interior cosmético |
Carbono forjado, tejido de sarga |
|
Áreas propensas a impactos |
Híbrido de carbono y kevlar |
|
Construcciones de autos de exhibición |
Carbono forjado, tejido de sarga |
|
Deportes de motor |
Kevlar de carbono |
|
Instalaciones de bricolaje |
Sarga 2x2, carbono forjado (precortado) |
Aplicaciones y casos prácticos: Cómo se utiliza la fibra de carbono en la construcción de automóviles
Fibra de carbono OEM vs. fibra de carbono del mercado de accesorios: ¿Cuáles son las diferencias en rendimiento y ajuste?
Componentes de fibra de carbono OEM: dónde los fabricantes los utilizan y por qué
-
Los autos deportivos y superdeportivos de alta gama de marcas como Ferrari, Lamborghini y McLaren incorporan paneles de carrocería de fibra de carbono, componentes aerodinámicos y molduras interiores para reducir el peso y mejorar el rendimiento.
-
Los fabricantes utilizan fibra de carbono preimpregnada de alta calidad, lo que garantiza una resistencia constante, ahorro de peso y un ajuste preciso.
-
Las piezas OEM se someten a pruebas exhaustivas de seguridad en caso de choque, aerodinámica y durabilidad, lo que las hace costosas pero altamente confiables.
-
La fibra de carbono se encuentra a menudo en capós, paneles de techo, alerones, divisores delanteros e incluso estructuras de chasis monocasco en modelos de alto rendimiento como el McLaren P1 y el Lamborghini Aventador.
Componentes de fibra de carbono para posventa: personalización y mejoras de rendimiento
-
El mercado de accesorios ofrece una variedad más amplia de tipos de fibra de carbono, incluidos el carbono húmedo, el carbono seco, el carbono forjado y el carbono Kevlar.
-
Las piezas de recambio pueden ser cosméticas o funcionales, y los kits aerodinámicos, capós, baúles, tapas de espejos y cubiertas del compartimento del motor son aplicaciones comunes.
-
El ajuste puede variar significativamente; las marcas de alta gama ofrecen fibra de carbono moldeada con precisión, mientras que las opciones de menor costo pueden sufrir patrones de tejido inconsistentes, ajuste imperfecto o peso adicional debido al uso excesivo de resina.
-
Muchos entusiastas de las pistas optan por capós y guardabarros de fibra de carbono de posventa para reducir el peso en construcciones orientadas al rendimiento.
¿Dónde se utiliza la fibra de carbono en los coches? Paneles de carrocería, molduras interiores y componentes estructurales
Paneles de carrocería: Los beneficios de la fibra de carbono en aplicaciones exteriores
-
Los capós, baúles, guardabarros y techos de fibra de carbono reducen significativamente el peso en comparación con las alternativas de acero o aluminio, lo que mejora el manejo y la aceleración.
-
La fibra de carbono de tejido sarga 2x2 es la opción más común debido a su alta resistencia a la tracción y durabilidad en los paneles estructurales de la carrocería.
-
La fibra de carbono forjada se utiliza más comúnmente para piezas exteriores cosméticas, como cubiertas de espejos, faldones laterales y divisores, ya que es menos rígida que la fibra de carbono tejida tradicional.
-
El híbrido de carbono y kevlar se utiliza a veces para la protección de los bajos, en coches de rally y en aplicaciones todoterreno, donde la durabilidad es más importante que el ahorro de peso.
Acabados interiores: atractivo estético vs. beneficios de rendimiento
-
Las piezas de acabado interior de fibra de carbono, como los paneles del tablero, las consolas centrales y los insertos de las puertas, son principalmente cosméticos.
-
El carbono forjado es cada vez más popular en las construcciones de alta gama debido a su apariencia moderna y lujosa.
-
La fibra de carbono con tejido sarga sigue siendo el estándar de la industria para una apariencia clásica y de alto rendimiento.
-
La fibra de carbono húmeda se usa a menudo en kits de acabado interior de posventa de menor costo, aunque carece del ahorro de peso y la resistencia de las opciones de carbono seco.
Componentes estructurales: cuando se utiliza fibra de carbono para chasis y refuerzos
-
Los superdeportivos y los coches de carreras OEM utilizan diseños de chasis monocasco totalmente de fibra de carbono, lo que reduce el peso y mantiene la resistencia.
-
Las barras de soporte y los refuerzos de chasis de fibra de carbono del mercado de accesorios ofrecen mejoras de rigidez con un mínimo aumento de peso.
-
La fibra de carbono con tejido de sarga es la opción preferida para los componentes estructurales, ya que proporciona el mejor equilibrio entre resistencia, peso y flexibilidad.
-
El carbono forjado rara vez se utiliza para piezas estructurales, ya que carece de la rigidez direccional necesaria para aplicaciones de soporte de carga.
¿Por qué la fibra de carbono domina el automovilismo? El papel de los compuestos ligeros en las carreras
Ahorro de peso y mejoras de rendimiento en las carreras
-
Cada libra ahorrada aumenta la aceleración, la eficiencia de frenado y la capacidad de tomar curvas, lo que convierte a la fibra de carbono en un material esencial en los deportes de motor.
-
Los autos de Fórmula 1 utilizan un chasis monocasco íntegramente de fibra de carbono, con fibra de carbono de tejido de sarga 2x2 estratificada estratégicamente para lograr la máxima resistencia con un peso mínimo.
-
Los autos de carreras GT y los vehículos de resistencia utilizan fibra de carbono para componentes aerodinámicos, como divisores, difusores y alerones, para maximizar la carga aerodinámica y minimizar la resistencia.
¿Por qué se prefiere el tejido de sarga 2x2 en los deportes de motor?
-
Proporciona el mejor equilibrio entre resistencia y peso, garantizando durabilidad bajo altas tensiones.
-
Ofrece alta resistencia a la tracción y rigidez, esencial para componentes aerodinámicos, refuerzos estructurales y piezas de chasis.
-
El carbono forjado rara vez se utiliza en los deportes de motor debido a su falta de rigidez direccional y su menor capacidad de carga.
Kevlar de carbono en aplicaciones de carreras de alto impacto
-
Se utiliza en coches de rally y carreras de resistencia, donde la resistencia al impacto es más importante que el simple ahorro de peso.
-
Se encuentra en la protección de bajos, revestimientos de huecos de ruedas y paneles de refuerzo para evitar daños causados por escombros y colisiones de alto impacto.
-
Proporciona un equilibrio entre durabilidad y construcción liviana, reduciendo el riesgo de falla estructural.
¿Qué estilos de fibra de carbono ofrecen el mejor valor para el rendimiento en la calle y las construcciones de exhibición?
Equilibrio entre rendimiento, costo y estética en construcciones de calle
-
La fibra de carbono con tejido de sarga 2x2 es ideal para autos de alto rendimiento que se conducen en la calle, ya que ofrece un equilibrio entre asequibilidad, reducción de peso y resistencia.
-
La fibra de carbono forjada es popular para vehículos de lujo y de exhibición, ya que proporciona una estética única y de alta gama sin ofrecer necesariamente ventajas de rendimiento.
-
Las piezas de fibra de carbono húmedas son más económicas, pero carecen del ahorro de peso y la durabilidad de las opciones de carbono seco de gama alta.
Las mejores opciones de fibra de carbono según su aplicación en automóviles de calle
|
Solicitud |
El mejor tipo de fibra de carbono |
|
Ahorro de peso y rendimiento |
Tejido de sarga 2x2 |
|
Construcciones de lujo y de exhibición |
Carbono forjado |
|
Diseño de interiores |
Carbono forjado, sarga 2x2 |
|
Componentes de chasis y aerodinámicos |
Tejido de sarga 2x2 |
|
Protección todoterreno o de alto impacto |
Híbrido de carbono y kevlar |
Puntos clave para elegir fibra de carbono en la construcción urbana
-
Los autos de calle enfocados en el rendimiento deberían priorizar la fibra de carbono con tejido de sarga 2x2 para lograr resistencia y reducción de peso.
-
Los coches de exhibición y los modelos de lujo son los que más se benefician del atractivo estético único del carbono forjado.
-
Los automóviles de calle que requieren durabilidad en áreas de alto impacto (uso fuera de carretera o en pista) deberían considerar materiales híbridos de carbono y kevlar.
-
Los constructores conscientes del presupuesto deben tener cuidado con la fibra de carbono aplicada en húmedo, ya que a menudo no proporciona un ahorro de peso significativo ni durabilidad a largo plazo.
El futuro de la fibra de carbono en aplicaciones automotrices
¿Cuáles son los próximos avances en la fabricación de fibra de carbono?
Técnicas avanzadas de producción de fibra de carbono
-
Tejido automatizado de alta velocidad: los nuevos sistemas de tejido robótico están aumentando la eficiencia de la producción, permitiendo una fabricación más rápida y precisa de estructuras complejas de fibra de carbono.
-
Compuestos de fibra de carbono impresos en 3D: las innovaciones en la fabricación aditiva (impresión 3D) están permitiendo la creación de piezas de fibra de carbono personalizadas con una orientación optimizada de las fibras, lo que reduce el desperdicio y mejora la relación resistencia-peso.
-
Infusión de resina y nanotecnología: la integración de nanopartículas en resina de fibra de carbono mejora la resistencia al calor, la resistencia y la durabilidad, haciéndola más adaptable para aplicaciones de alto rendimiento y condiciones extremas.
-
Métodos de curado fuera de autoclave (OOA): se están desarrollando nuevas técnicas de curado para reducir la dependencia de costosos sistemas de autoclave, lo que hace que la fabricación de fibra de carbono de alta calidad sea más rentable y escalable.
Compuestos de fibra de carbono de próxima generación
-
Fibra de carbono autorreparadora: los investigadores están desarrollando fibra de carbono con microcápsulas integradas de agentes curativos que pueden reparar pequeñas grietas automáticamente, lo que extiende la vida útil de los componentes de carbono.
-
Materiales híbridos de fibra de carbono: se está explorando el uso de fibra de carbono con infusión de grafeno para crear materiales más livianos y más fuertes con conductividad eléctrica mejorada, lo que abre posibilidades para la integración en carcasas de baterías de vehículos eléctricos (VE) y sistemas de sensores.
¿Es posible hacer la fibra de carbono más sostenible? La demanda de alternativas ecológicas
Desafíos de la sostenibilidad de la fibra de carbono
-
Alto consumo de energía en la producción: El proceso de carbonización requiere temperaturas extremas, lo que hace que la fabricación de fibra de carbono requiera un alto consumo energético.
-
Procesos de reciclaje difíciles: a diferencia de los metales, los compuestos de fibra de carbono son difíciles de reciclar, ya que no se funden ni se reforman como el aluminio o el acero.
-
Impacto ambiental de las materias primas: La producción de fibras de poliacrilonitrilo (PAN), el principal precursor de la fibra de carbono, implica un importante procesamiento químico y emisiones.
Avances en el reciclaje y la sostenibilidad de la fibra de carbono
-
Fibra de carbono reciclada (rCF): las empresas están desarrollando métodos para reprocesar los desechos de fibra de carbono en nuevos materiales, lo que la convierte en una opción viable para aplicaciones de menor estrés, como paneles interiores, molduras y componentes de la parte inferior de la carrocería.
-
Fibra de carbono de origen biológico: la investigación sobre precursores de fibra de carbono derivados de plantas, como los compuestos basados en lignina, está mostrando potencial para reducir las emisiones de producción y crear materiales de fibra de carbono más sostenibles y renovables.
-
Fabricación de fibra de carbono con bajas emisiones: algunos fabricantes están invirtiendo en hornos de carbonización alimentados eléctricamente, lo que podría reducir significativamente la huella de carbono de la producción.
¿Cómo influirá la fibra de carbono en el futuro de los vehículos eléctricos y autónomos?
Fibra de carbono en vehículos eléctricos ligeros (VE)
-
Carcasas de batería y estructuras de seguridad: Se utiliza fibra de carbono para crear carcasas de batería livianas y resistentes a los impactos, lo que reduce el peso total del vehículo y mantiene la integridad estructural.
-
Componentes del chasis y la carrocería: los fabricantes de vehículos eléctricos recurren cada vez más a monocascos de fibra de carbono y diseños aeroeficientes para ampliar la autonomía y la eficiencia de la batería.
-
Beneficios del aislamiento térmico y eléctrico: Los compuestos de fibra de carbono se están diseñando con propiedades resistentes al calor y no conductoras, lo que mejora la gestión térmica en los sistemas de propulsión de los vehículos eléctricos.
El papel de la fibra de carbono en los vehículos autónomos
-
Aligeramiento para mayor autonomía: los vehículos eléctricos autónomos se benefician de la reducción de peso, ya que un menor peso significa una mayor eficiencia para los sistemas alimentados por batería.
-
Carcasa de sensores y refuerzos estructurales: Se está incorporando fibra de carbono en carcasas de sensores reforzadas y plataformas de vehículos impulsadas por IA, lo que ayuda a mantener la durabilidad y al mismo tiempo minimiza la interferencia con los componentes electrónicos.
-
Absorción de impactos y seguridad: Los vehículos autónomos de próxima generación pueden presentar estructuras de fibra de carbono diseñadas para absorber el impacto de manera más efectiva que los marcos tradicionales de acero o aluminio.
¿Se volverá más asequible la fibra de carbono? Predicciones de precios y crecimiento del mercado
Tendencias del mercado en precios de la fibra de carbono
-
El aumento de la demanda reduce los costos: a medida que más fabricantes adopten la fibra de carbono, las economías de escala probablemente reducirán los costos, haciéndola más accesible para la producción de vehículos convencionales.
-
Avances en la eficiencia de fabricación: Se espera que el tejido automatizado, el curado fuera de autoclave y los materiales híbridos reduzcan los costos de producción, haciendo que los componentes de fibra de carbono de alta calidad sean más asequibles.
-
Crecimiento de la fibra de carbono reciclada: La introducción de compuestos de fibra de carbono reciclada probablemente creará una alternativa de menor costo para aplicaciones no estructurales, aumentando su accesibilidad.
Accesibilidad futura en la automoción y los deportes de motor
-
Expansión más allá del lujo y los superdeportivos: si bien actualmente está dominado por fabricantes de alta gama, se espera que el uso de fibra de carbono se extienda a los autos deportivos de gama media e incluso a algunos vehículos de consumo a medida que disminuyan los costos.
-
Mayor presencia en la industria del mercado de accesorios: piezas de fibra de carbono más asequibles y de alta calidad estarán ampliamente disponibles para los entusiastas, ofreciendo mayor resistencia y menor peso a precios competitivos.
-
Innovación continua en vehículos de carreras y de alto rendimiento: los equipos de deportes de motor seguirán llevando la fibra de carbono hasta sus límites, impulsando nuevos avances en materiales livianos y compuestos híbridos para aplicaciones futuras.
Conclusión: La evolución de la fibra de carbono en el mundo del automóvil
-
Se prevé que la fibra de carbono siga siendo un material dominante en el rendimiento, los deportes de motor y el diseño de vehículos futuros.
-
Las innovaciones en fabricación, sostenibilidad y materiales alternativos impulsarán una mayor accesibilidad y adopción tanto en los sectores OEM como en el mercado de repuestos.
-
A medida que los vehículos eléctricos y autónomos evolucionan, el papel de la fibra de carbono en el aligeramiento, la integridad estructural y la eficiencia energética seguirá expandiéndose.
Conclusión: Cómo elegir la fibra de carbono adecuada para el rendimiento, la estética y el presupuesto
¿Qué tipo de fibra de carbono es mejor para tu proyecto? Conclusiones clave y recomendaciones finales
-
Fibra de carbono de tejido de sarga 2x2: Ofrece el mejor equilibrio entre resistencia, ligereza y precio asequible, lo que la convierte en la fibra de carbono más versátil y utilizada. Es ideal para componentes estructurales, paneles de carrocería y construcciones de alto rendimiento.
-
Fibra de carbono forjada: Ofrece una estética única y marmolada, además de una alta resistencia al impacto, pero carece de la resistencia a la tracción y la rigidez de la fibra de carbono tejida. Es ideal para mejoras estéticas, molduras y construcciones de lujo.
-
Híbrido de carbono y kevlar: combina la resistencia de la fibra de carbono con la durabilidad del Kevlar, lo que lo convierte en la opción preferida para áreas de alto impacto, aplicaciones todoterreno y construcciones de deportes de motor que requieren resistencia adicional a la abrasión.
-
Otras variaciones de fibra de carbono: Se utilizan tejidos especializados, estructuras de núcleo de panal y materiales híbridos en aplicaciones específicas donde la flexibilidad, el ahorro de peso o el refuerzo son prioridades.
¿Cuáles son las mejores opciones de fibra de carbono para cada presupuesto?
|
Caso de uso |
El mejor tipo de fibra de carbono |
¿Por qué? |
|
Construcciones de alto rendimiento |
Tejido de sarga 2x2 |
Relación resistencia-peso superior para un mejor rendimiento |
|
Componentes estructurales y piezas aerodinámicas |
Tejido de sarga 2x2 |
Alta resistencia a la tracción y rigidez. |
|
Autos de exhibición y creaciones de lujo |
Carbono forjado |
Apariencia única con atractivo premium. |
|
Diseño y acabado interior |
Carbono forjado, tejido de sarga 2x2 |
Versatilidad estética |
|
Protección todoterreno y de alto impacto |
Híbrido de carbono y kevlar |
Mayor durabilidad y resistencia a la abrasión. |
|
Modificaciones fáciles de hacer |
Sarga 2x2, carbono forjado (precortado) |
Instalación y disponibilidad más sencillas |
|
Deportes de motor y uso de la pista |
Sarga 2x2, híbrido de carbono y kevlar |
Materiales de alta resistencia para rendimiento y durabilidad. |
Consideraciones presupuestarias
-
Entusiastas con un presupuesto limitado: los compuestos de fibra de carbono húmeda o reforzados con fibra de vidrio pueden ofrecer una apariencia de carbono a un costo menor, pero carecen de los beneficios de rendimiento de la fibra de carbono real.
-
Constructores de gama media: la fibra de carbono con tejido de sarga 2x2 ofrece la mejor relación costo-rendimiento, lo que la convierte en una excelente opción para componentes aerodinámicos, paneles de carrocería y piezas de decoración.
-
Construcciones personalizadas y de alta gama: la fibra de carbono forjada y los materiales híbridos ofrecen exclusividad y un estilo único, pero a un costo mayor.
¿Cómo deben los entusiastas, corredores y constructores profesionales seleccionar la fibra de carbono?
Para entusiastas y constructores callejeros
-
La fibra de carbono con tejido de sarga 2x2 es la mejor opción para la mayoría de los entusiastas debido a su resistencia, asequibilidad y disponibilidad.
-
La fibra de carbono forjada es una excelente opción para acabados interiores, detalles exteriores y construcciones centradas en el lujo que priorizan la estética.
-
El híbrido de carbono y kevlar es el más adecuado para aplicaciones todoterreno, competiciones de rally y áreas expuestas a altos impactos o abrasión.
Para constructores profesionales y aplicaciones de deportes de motor
-
La fibra de carbono con tejido de sarga 2x2 sigue siendo el estándar de la industria para el refuerzo de chasis, componentes aerodinámicos y paneles de carrocería en aplicaciones de alto rendimiento.
-
El híbrido de carbono y kevlar es la mejor opción para entornos de alto estrés, especialmente en aplicaciones de carreras, todoterreno y resistencia.
-
La fibra de carbono forjada se debe utilizar cuando se necesita resistencia al impacto pero el ahorro de peso y la rigidez son menos críticos.
Para fabricación personalizada y construcciones avanzadas
-
Los constructores que buscan piezas de fibra de carbono completamente personalizadas deberían considerar tejidos híbridos, estructuras de panal o compuestos reforzados, según la aplicación.
-
Los profesionales que utilizan fibra de carbono estructural deben garantizar la aplicación adecuada de la resina, los métodos de curado y las técnicas de fabricación para mantener la resistencia y la longevidad.
¿Qué le depara el futuro a la fibra de carbono? El futuro de los materiales ligeros de alto rendimiento.
-
La fibra de carbono sigue siendo un material líder en los deportes de motor, los vehículos de alto rendimiento y la personalización de lujo.
-
Los avances en la fabricación, la sostenibilidad y los materiales híbridos harán que la fibra de carbono sea más accesible al tiempo que mejorarán su durabilidad y eficiencia.
-
A medida que evolucionen los vehículos eléctricos y autónomos, la fibra de carbono desempeñará un papel más importante en la ingeniería de aligeramiento, seguridad y rendimiento.
Elegir el tipo correcto de fibra de carbono depende del propósito de tu construcción, tu presupuesto y tus necesidades de rendimiento. Ya sea por rendimiento, estética o durabilidad, seleccionar el tejido y el material adecuados garantiza el mejor equilibrio entre resistencia, ahorro de peso y durabilidad.
¡Compre nuestras piezas de carbono hoy!
Por qué elegir la fibra de carbono adecuada es importante para tu proyecto
La fibra de carbono no solo es estética: es un material de alto rendimiento que mejora la resistencia, reduce el peso y la durabilidad. Ya sea que busques reducir peso para un mejor manejo, añadir un estilo agresivo o reforzar componentes críticos, elegir la fibra de carbono adecuada es clave para sacar el máximo provecho de tu equipo.
Desde el tejido de sarga 2x2 para mayor resistencia y fiabilidad hasta el carbono forjado para una estética moderna y de alta gama, cada tipo de fibra de carbono tiene sus ventajas. Sean cuales sean tus objetivos de conducción (rendimiento en pista, estilo de coche de exhibición o uso diario en la calle), invertir en las piezas de fibra de carbono adecuadas llevará tu auto al siguiente nivel.
Encuentre piezas de fibra de carbono de alta calidad para su construcción
En JD Customs USA, ofrecemos componentes premium de fibra de carbono diseñados para ofrecer funcionalidad y estilo. Ofrecemos una cuidada selección de piezas de fibra de carbono de alto rendimiento, que incluyen:
-
Paneles de carrocería ligeros para reducción de peso y aerodinámica.
-
Piezas de acabado interior para una apariencia de alto rendimiento y alta gama
-
Componentes aerodinámicos como divisores y alas para una mayor carga aerodinámica
-
Herrajes de titanio y fibra de carbono para completar los detalles.
Descubra nuestras piezas de fibra de carbono más vendidas
Capó de fibra de carbono estilo OEM JDC (Evo 8/9) : capó ligero de fibra de carbono para Mitsubishi Evo 8/9 
-
Características: ahorro de peso significativo, estilo agresivo, ajuste de precisión.
-
Beneficios: reduce el peso de la parte delantera para mejorar el manejo y la aerodinámica.
-
Por qué a los clientes les encanta: tejido de alta calidad, ajuste estilo fábrica, fácil instalación.
Baúl de fibra de carbono estilo Seibon CSL (Evo X) – Tapa del maletero de fibra de carbono para Evo X 
-
Características: construcción duradera, elegante acabado de fibra de carbono, peso reducido.
-
Beneficios: mejora la aerodinámica trasera manteniendo los puntos de montaje de fábrica.
-
Por qué es un éxito de ventas: equilibrio perfecto entre rendimiento y estética.
Las mejores mejoras aerodinámicas de fibra de carbono
Divisor de viento delantero APR (MK5 Supra) : Divisor delantero de fibra de carbono para A90 Supra 
-
Características: diseño inspirado en las carreras, construcción de fibra de carbono de alta resistencia.
-
Beneficios: agrega carga aerodinámica en la parte delantera para una mejor estabilidad a alta velocidad.
-
Lo que lo distingue: contorno perfecto para montaje OEM+.
Alerón de maletero de fibra de carbono Rexpeed V1 (22+ GR86/BRZ) – Alerón/ala de fibra de carbono para GR86/BRZ 
-
Características: aerodinámica probada en pista, ligero pero duradero.
-
Beneficios: mejora el agarre trasero y la estabilidad a alta velocidad.
-
Por qué es imprescindible: mejora tanto el rendimiento como el estilo.
Los mejores interiores y piezas de decoración de fibra de carbono
Volante de fibra de carbono JDC (Evo 7/8/9) – Volante de fibra de carbono para Evo 7/8/9 
-
Características: diseño ergonómico, opciones de agarre en Alcantara o cuero, construcción liviana de fibra de carbono.
-
Beneficios: mejora la sensación de conducción, reduce el peso y añade un aspecto de alta gama.
-
Por qué los entusiastas lo adoran: actualización perfecta tanto para uso en calle como en pista.
Por qué estos productos de carbono se destacan
-
Seleccionados a mano por su calidad y rendimiento: no hay imitaciones baratas ni piezas mal fabricadas.
-
Diseñado para un ajuste preciso, lo que garantiza una fácil instalación y una integración perfecta con los componentes OEM.
-
De confianza para entusiastas y constructores profesionales, con comentarios positivos de los clientes y durabilidad comprobada.







Share:
Las mejores mejoras de fibra de carbono para el Nissan 370Z
Guía de JDC para la personalización de ruedas: Actualice sus ruedas sin reemplazarlas